Brief history and geography of France. France. Geography, description and characteristics of the country. France, general information
Official name - French Republic(Republique Francaise, French Republic). Located in the western part of Europe. Area 547 thousand km2, population 59.7 million people. (2002). Official language- French. The capital is Paris (9.6 million people). Public holiday - Bastille Day on July 14th. The monetary unit is the euro (since 2002, before that the French franc).
An integral part of France are the overseas territories (French Polynesia, Southern and Atlantic territories, New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna Islands), overseas departments (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique) and territorial communities (Mayotte, Saint-Pierre and Miquelon). The total area is 4 thousand km2, the population is 1.8 million people.
Member of the UN (since 1945), IMF and World Bank (since 1947), NATO (1949-66), ECSC (since 1951), OECD (since 1961), EU (since 1957), OBSS (since 1973), G7 "(since 1975), EBRD (since 1990), WTO (since 1995).
Sights of France
Geography of France
Located between 42°20’ and 51°5’ north latitude; 4°27 'west and 8°47' east longitude. In the north, the territory of France is washed by the North Sea straits of Pas de Calais and the English Channel, in the west by the Bay of Biscay and the Atlantic Ocean, and in the south by the Mediterranean Sea. The length of the coastline is 3427 km. France borders Andorra, Spain, Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Monaco, Italy, and Switzerland.
All types of Western European landscapes are found in France. The central, eastern and southern parts are distinguished by hilly or mountainous terrain. The largest in area mountainous region- Central French Massif (highest point - Mount Puy de Sancy, 1886 m) - basalt plateaus alternating with volcanic cones, plateaus, and rivers of the Loire basin. In the southeast stretch the high-altitude Alps (Mont Blanc, 4807 m), framed in the west by mid-altitude ridges - the Pre-Alps, which continue in the north with the Jura and Vosges mountains (Ballon de Guerbiller, 1423 m). The southwest is occupied by the Pyrenees (Vinmal, 3298 m).
North and west, almost 2/3 of France, low and high plains; the largest of them is the Paris Basin. In the southwest, parallel to the Bay of Biscay, stretch the coastal plains of Aquitaine (Landes) with a chain of dunes up to 100 m high. In the northwest, the plains pass into the Armorican Upland, washed by the straits of the North Sea. In the southwest and south, the Rhône and Languedoc lowlands merge. A small part of the Upper Rhine Lowland enters the territory of France.
The main rivers are: Loire (1000 km), Rhone (812 km, including 522 km in France), Seine (776 km) and Garonne with its mouth called the Gironde (650 km). In the east lies part of the middle course of the Rhine. Also located in France South part Lake Geneva.
20% of France's territory is covered by forests, concentrated mainly in the western regions of Aquitaine, in the eastern part of the Paris Basin, in the Alps and the Pyrenees. The upper limit of forests is 1600-1900 m above sea level in the Alps, 1800-2100 m in the Pyrenees. Higher up they turn into subalpine shrubs, and at an altitude of 2100-2300 m into alpine meadows. Shrub thickets and sparse forests (evergreen species of oak and pine) are typical for the Mediterranean south. The characteristic landscape of the north-west is heathland and meadows.
The main representatives of the fauna of France are concentrated in forested areas, especially in the mountains. Mammals: wild forest cat, fox, badger, ermine, red deer, roe deer, fallow deer, wild boar, squirrel, hare; in the highlands - chamois, mountain goat, alpine marmot. There are numerous birds: hawks, kites, partridges, hazel grouse, snipe. Common river fish include perch, pike, pike perch, and trout; in the seas surrounding France - tuna, mackerel, sardine, cod, flounder.
In the depths of France lie a variety of minerals. Reserves of gas, iron ore, bauxite, uranium, and potassium salts are identified.
France has several climate zones. The western part is dominated by a maritime climate; in the central and eastern regions - transitional from maritime to continental. Stable snow cover persists in winter in the Massif Central, the Alps and the Pyrenees. In the mountains, the climate changes significantly with altitude up to the alpine climate. The south of the Rhone Lowland and the Mediterranean coast are dry subtropics.
Population of France
Population density 107 people. per 1 km2, which is 2-3 times lower than in neighboring countries, although in some areas (Paris Basin, Provence, Côte d'Azur) the density is several times higher than average. 75% of the population lives in cities (2002).
The population movement of France has historically been characterized by alternating long-term sharp rises and strong declines. The demographic increase for 1896-1946 was only 0.3 million people, and for 1946-2002 - 20 million people. The bulk of the increase occurred in the 1950-70s, in 1980-2002 - only 4.9 million people.
Natural population growth is 4% with a birth rate of 13% and a death rate of 9%. The persistence of a relatively high level of natural growth is explained by long-term positive changes in the population reproduction regime and the expansion of immigration. The improvement in the reproduction regime is manifested in a fairly high (for a European country) birth rate, despite a decrease in the number of marriages and an increase in divorces, an increase in the average age of marriage, and an increase in women’s participation in social production. There is a steady decline in mortality rates due to a decrease in infant mortality (4 people per 1000 births) and an increase in average life expectancy. The latter is 79.05 years (including 75.17 years for men and 82.5 years for women), one of the first places in the world.
The ratio of men to women is 48.6: 51.4. The age structure is characterized by a pronounced tendency towards aging. The proportion of persons aged 0-14 years is 18.5%, 15-64 years - 65.2%, 65 years and older - 16.3% (2002).
Due to the rapid increase in the importance of older generations, the growth of the economically active population lags behind the overall population growth. Number of employees: 26.6 million people. Only 45.8% of the economically active population is in the most working age (20-60 years), and 40.6% of this group are people aged 40 years and older.
According to forecasts, if current demographic trends continue, the population of France will increase by only 5 million people by 2050. At the same time, at least 1/3 of the population will be over 60 years old, and only 20% will be under 20. The economically active population will grow until 2006, and then begin to decline (by 2020 by 750 thousand people compared to 2002).
An important component of the demographic situation in France is immigration, which ensured the 2nd half. 20th century OK. 1/4 of population growth. In the 1980s - mid. 90s the annual influx of immigrants amounted to 100 thousand people, from the middle. 1990s as a result of government restrictions, it decreased to 50 thousand people. In 2002, there were 3.3 million resident foreigners in France, i.e. residents who have not received citizenship rights. It is purchased annually approx. 100 thousand people; Official statistics classify their children and grandchildren as French. Taking into account such categories, at least 15 million people from other countries now live in France - almost 25% of the population.
In 2002, 40.3% of immigrants were Europeans (mainly from Portugal, Spain and Italy), 43% were Africans (mainly from Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia). Immigrants, especially those from African countries, have low manufacturing skills; the possibility of their employment in the conditions of the current stage of scientific and technological revolution is small, and adaptation to the norms of life of their new homeland is difficult due to deep intercultural differences. The socio-economic problems that arise in this regard (unemployment, crime) are manifested in political life by the accelerated growth of the influence of far-right parties.
France is characterized by a high level of educational preparation of the population. In 2002, the education system covered 14 million 390 thousand pupils and students, St. 1 million teachers, professors. 6.6% of residents have higher education, 15.1% have specialized secondary education. In 2002, 79% of lyceum graduates became bachelors. In terms of the total amount of spending on education and their share in GDP, France is one of the first places in the world.
The overwhelming majority of the population are French. Several small ethnic minorities arose historically in border areas, many of which formerly belonged to other countries. Now minorities do not exceed 6.5% of the country's population. The largest are the Alsatians, as well as the Bretons, Flemings, Corsicans, Basques and Catalans. Their cultural characteristics, traditions, languages are considered in France as important elements of the common cultural heritage and are carefully preserved.
By religion, the vast majority of French people are Catholics (83-88%). The second largest denomination is Muslims, far ahead of Protestants and Jews (5-10, 2 and 1% of the population, respectively).
History of France
The territory of France has been inhabited by people since ancient times. The first known people to settle on it were the Celts (from the 6th-5th centuries BC). Their Roman name - Gauls - gave the name to the country (the ancient name of France is Gaul). All R. 1st century BC. Gaul, conquered by Rome, became its province. For 500 years, the development of Gaul went under the sign of Roman culture - general, political, legal, economic. In the 2nd-4th centuries. AD Christianity spread in Gaul.
In con. 5th century Gaul, conquered by the Germanic Frankish tribes, became known as the Frankish Kingdom. The leader of the Franks was a talented military leader, an intelligent and prudent politician, Clovis from the Merovingian dynasty. He largely preserved Roman laws and established social relations, and was the first of the German leaders in the former Roman Empire to form an alliance with the Roman Catholic Church. The mixing of the Franks with the Halo-Roman population and the merging of their cultures created a kind of synthesis - the basis for the formation of the future French nation.
Since the death of Clovis in the beginning. 6th century The Frankish kingdom was subject to continuous divisions and reunifications, and was the scene of countless wars of various branches of the Merovingians. K ser. 8th century they have lost power. Charlemagne, who gave the name to the new Carolingian dynasty, founded a huge empire consisting of almost all of modern France, part of Germany and, as tributaries, Northern and Central Italy and the Western Slavs. After his death and the division of the empire (843), the West Frankish kingdom emerged as an independent state. This year is considered the starting point of French history.
K con. 10th century the Carolingian dynasty was interrupted; Hugo Capet was elected king of the Franks. The Capetians (their various branches) that originated from him reigned until the Great French Revolution (1789). In the 10th century their kingdom became known as France
France of the era of the first Capetians, formally united, was actually divided into a number of independent feudal estates. The kings' desire for centralization ensured the gradual overcoming of feudal fragmentation and the formation of a single nation. The hereditary possession of the kings (domain) expanded through dynastic marriages and conquests. Endless wars and the needs of the growing state apparatus required more and more financial resources. K con. 13th century taxation of the clergy caused a sharp protest from Pope Boniface. Trying to enlist the support of the population in the fight against the pope, King Philip IV the Fair (1285-1303) convened the Estates General in 1302 - representation of all 3 estates. So France became a class monarchy.
To the beginning 14th century France was the most powerful state in Western Europe. But her further development slowed down due to the Hundred Years' War with England (1337-1453), which took place entirely on French territory. By 1415, the British had captured almost all of France and threatened its existence as a sovereign state. However, under the leadership of Joan of Arc, French troops achieved a turning point in military operations, which ultimately led to the victory of the French and the expulsion of the British.
K con. 15th century the completion of centralization determined the autonomy of the royal financial apparatus from class representation and the virtual cessation of the activities of the Estates General. The transformation of the class monarchy into an absolute monarchy began.
In con. 15 - mid. 16th century France, which tried to achieve hegemony in Europe and annex Northern Italy, fought the Italian Wars with Spain and the Holy Roman Empire (1494-1559). Without bringing any political results, they completely depleted the financial resources of France, which led to a sharp deterioration economic situation countries. The growth of social protest was closely intertwined with the spread of reform ideas. The split of the population into Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots) resulted in the long Wars of Religion (1562-91), which culminated in the massacre of Huguenots in Paris (St. Bartholomew's Night, 1572). In 1591, a representative of the younger branch of the Capetians, Henry Bourbon, a Huguenot leader who converted to Catholicism, was proclaimed king of France under the name of Henry IV. The Edict of Nantes (1598), which he issued, equalized the rights of Catholics and Huguenots, putting an end to confrontation on religious grounds.
17th century was a time of strengthening of French absolutism. In the 1st third of it, Cardinal Richelieu, who actually ruled the country under Louis XIII, basically eradicated the noble opposition; its last manifestation was the Fronde - a mass movement led by the princes of the blood (1648-53), after the defeat of which the great nobility lost political significance. Absolutism reached its peak during the independent reign of Louis XIV (1661-1715). Under him, the nobility was not allowed to govern the country; it was carried out by the “Sun King” himself, who relied on secretaries of state and the Comptroller General of Finance (this post was held for 20 years by J.-B. Colbert, an outstanding financier and mercantilist who did a lot for the development of French industry and trade).
In the 17th century France waged wars in Europe aimed either at eliminating the dominance of other states (the Thirty Years' War) or at ensuring its own hegemony (with Spain in 1659, the Dutch Wars in 1672-78 and 1688-97). All territorial gains gained during the Dutch Wars were lost as a result of the War of the Spanish Succession (1701-14).
From the 2nd half. 18th century Absolutism, which had become obsolete, was experiencing an acute spiritual and economic crisis. In the spiritual sphere, its expression was the appearance of a galaxy of philosophers and writers who rethought the acute problems of social life (the Age of Enlightenment). In the economy, persistent budget deficits, prolonged increases in taxes and prices, coupled with prolonged crop failures, caused mass impoverishment and starvation.
In 1789, in an atmosphere of sharp aggravation of the socio-economic situation, under pressure from the Third Estate (merchants and artisans), the Estates General was convened after a many-year break. Deputies from the Third Estate declared themselves a National Assembly (June 17, 1789), and then a Constituent Assembly, which adopted the Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen. The rebellious people took and destroyed the symbol of the “old regime”, the royal prison Bastille (July 14, 1789). In August 1792, the monarchy was overthrown (King Louis XVI was executed); in September, the Republic was proclaimed. The uprising of the extreme left of its supporters led to the establishment of the bloody Jacobin dictatorship (June 1793 - July 1794). After the coup of July 27-28, 1794, power passed to the more moderate Thermidorians, and in 1795 to the Directory. A new coup, which led to the fall of the Directory (November 1799), turned France into a Consulate: the government was concentrated in the hands of 3 consuls; Napoleon Bonaparte assumed the functions of First Consul. In 1804 Bonaparte was proclaimed emperor, France turned into an empire.
During the period of the Consulate and the Empire, continuous Napoleonic wars were fought. Constant conscription into the army, rising taxes, and the unsuccessful Continental Blockade depleted France's strength; The defeat of Napoleonic troops (Great Army) in Russia and Europe (1813-14) accelerated the collapse of the empire. In 1814 Napoleon abdicated the throne; The Bourbons returned to power. France became a (constitutional) monarchy again. Napoleon's attempt to regain his throne (1815) was unsuccessful. According to the decisions of the Congress of Vienna (1815), France was returned to the borders of 1790. But the main achievements of the revolution - the abolition of class privileges and feudal duties, the transfer of land to peasants, legal reforms (Civil and other Napoleonic codes) - were not canceled.
In the 1st half. 19th century France was rocked by revolutions. The July Revolution (1830) was caused by attempts by Bourbon supporters (royalists) to restore the “old regime” in its entirety. It cost the power of the main branch of the Bourbons, who were finally overthrown by the revolution of 1848. Napoleon's nephew, Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte, became the president of the newly proclaimed Second Republic. After the coup d'état of 1851 and the subsequent year of military dictatorship, Louis Napoleon was crowned emperor under the name Napoleon III. France became an empire again.
The Second Empire (1852-70) was a period of rapid development of capitalism (mainly financial speculative), the growth of the labor movement and wars of conquest (Crimean, Austro-Italian-French, Anglo-French-Chinese, Mexican, Indochina War). Defeat in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870 and the unfavorable Peace of Frankfurt (1871) were accompanied by a failed attempt to overthrow the government (Paris Commune).
In 1875 the Constitution of the Third Republic was adopted. In the last quarter of the 19th century. power in France has stabilized. This was an era of widespread external expansion in Africa and South-East Asia and the formation of the French colonial empire. The question of the optimal form of government, not fully resolved by the nation, resulted in a fierce struggle between clerical monarchists and anti-clerical republicans. The Dreyfus Affair, which sharply aggravated this conflict, brought France to the brink of civil war.
In the 20th century France entered as a colonial empire, at the same time having an agrarian-industrial economy that lagged behind the leading industrial powers in industrial development. The rapid growth of the labor movement was expressed in the formation in 1905 of the Socialist Party (SFIO, the French section of the Socialist International). That same year, anti-clericals won a long-term dispute: a law on the separation of church and state was passed. In foreign policy, rapprochement with Great Britain and Russia marked the beginning of the Entente (1907).
On August 3, 1914, France joined the 1st world war, which it completed 4 years later, in November 1918, as a victorious power (along with Great Britain and the USA). The Treaty of Versailles of 1918 returned Alsace and Lorraine to France (which had gone to Prussia in the Frankfurt Peace). She also received part of the German colonies in Africa and large reparations.
In 1925, France signed the Locarno Treaties, which guaranteed Germany's western borders. At the same time, colonial wars were fought: in Morocco (1925-26) and in Syria (1925-27).
The war, having significantly pushed the development of the previously lagging French industry, ensured acceleration economic development. Positive structural changes in the economy - the transformation of France into an industrial-agrarian power - were accompanied by the growth of the labor movement. In 1920 the French Communist Party (PCF) was founded. The Great Depression began in France later than in other countries and was less acute, but longer lasting. OK. 1/2 of wage earners turned out to be underemployed, almost 400 thousand were unemployed. Under these conditions, the labor movement intensified. Under the leadership of the PCF, the Popular Front association was created, which won the parliamentary elections of 1936 by a large margin. On June 7, 1936, trade unions and employers signed the Matignon Agreements, which provided for a wage increase of 12%, 2-week paid holidays, the conclusion of collective agreements, the introduction of 40 -hour work week. The Popular Front was in power until February 1937.
In 1938, French Prime Minister Daladier, together with N. Chamberlain, signed the Munich Agreements, aimed at postponing the war in Europe. But on September 3, 1939, F., fulfilling its allied obligations towards Poland, declared war on Germany. The “strange war” (an inactive stay in the trenches on the fortified Franco-German border - the Maginot Line) lasted several months. In May 1940, German troops bypassed the Maginot Line from the north and entered Paris on June 14, 1940. On June 16, 1940, Prime Minister P. Reynaud transferred power to Marshal A. Petain. According to the truce concluded by Petain, Germany occupied ca. 2/3 of French territory. The government, which moved to the city of Vichy, located in the unoccupied zone, pursued a policy of cooperation with the fascist powers. On November 11, 1942, German and Italian troops occupied the unoccupied part of France.
From the beginning of the occupation, the Resistance movement operated in France, the largest organization of which was the National Front created by the PCF. General Charles de Gaulle, who served as Deputy Minister of Defense before the war, spoke on the radio from London on June 18, 1940, calling on all French people to resist the Nazis. De Gaulle, through great efforts, managed to create the Free France movement in London (from July 1942 - Fighting France) and ensure the accession of military units and the administration of a number of French colonies in Africa to it. On June 3, 1943, while in Algeria, de Gaulle formed the French Committee for National Liberation (FCNL). On June 2, 1944, the FKNO, recognized by the USSR, Great Britain and the USA, was transformed into the Provisional Government of the French Republic.
With the landing of Allied troops in Normandy (June 6, 1944), Resistance units went on the offensive throughout the country. During the Paris Uprising (August 1944), the capital was liberated, and in September all of France.
After liberation, the extremely difficult economic situation, combined with the high prestige of the communists and socialists, who did a lot for victory, guaranteed them massive voter support. The left was in power from 1945-47. In 1946, the Constitution of the IV Republic was adopted, which provided for the responsibility of the government to parliament (parliamentary republic). The Constitution proclaimed, along with civil liberties, socio-economic rights: to work, rest, health care, etc. Widespread nationalization was carried out. In May 1947, when the communists left the government and were replaced by representatives of the Rally of the French People party created by de Gaulle, the government course moved to the right. In 1948, an agreement on Franco-American cooperation (Marshall Plan) was signed.
In 1946-54, France fought a colonial war in Indochina, which ended with the recognition of the independence of the former colonies. From the beginning 1950s The national liberation movement in North Africa intensified. Morocco and Tunisia were granted independence (1956). Since 1954, fighting has been going on in Algeria, where France could not achieve success. The war in Algeria again split the country, parties and parliament, causing continuous governmental leapfrog. The attempt of the government of F. Gaillard to grant independence to Algeria caused a rebellion of the Algerian French - supporters of its preservation as part of France, supported by the command of the French troops in Algeria. They demanded the creation of a government of national salvation headed by de Gaulle. On June 1, 1958, the National Assembly granted de Gaulle the appropriate powers. By September 1958, his team had prepared a draft of a new Constitution, which provided for a radical change in the balance of power between the branches of government in favor of the executive branch. The project was put to a referendum on September 28, 1958; it was approved by 79.25% of the French who took part in the vote. Thus began a new period in the history of France - the V Republic. Charles de Gaulle (1890-1970), one of the outstanding political figures of the 20th century, was elected president of the country. The party he created, RPR, was transformed into the Union for new republic(UNR), became the ruling party.
In 1959, France announced recognition of the right of the Algerian people to self-determination. In 1962, the Evian Agreements on the cessation of hostilities were signed. This meant the final collapse of the French colonial empire, from which all the colonies in Africa had left even earlier (in 1960).
Under de Gaulle's leadership, France pursued an independent foreign policy. She came out of the military
NATO organization (1966), condemned the US intervention in Indochina (1966), took a pro-Arab position during the Arab-Israeli conflict (1967). After de Gaulle's visit to the USSR (1966), a Franco-Soviet political rapprochement emerged.
In the economic sphere, the course was taken towards the so-called. dirigisme is large-scale government intervention in reproduction. The state often tried to replace business and viewed it as a junior partner in economic activity. This policy, which ensured industrialization from the end. 1950s, towards the end. The 1960s turned out to be ineffective - France began to lag behind both in economic development and social transformations. In May 1968, the country was rocked by an acute socio-political crisis: violent student unrest and a general strike. The President dissolved the National Assembly and called early elections. They showed the strengthening of the position of the UNR (since 1968 - the Union of Democrats for the Republic, YDR), which won St. 70% of mandates. But de Gaulle's personal authority was shaken. In an effort to strengthen it, the president decided to hold a referendum on administrative-territorial reform and Senate reform (April 1969). However, the majority of French people (53.17%) opposed the proposed reforms. On April 28, 1969, de Gaulle resigned.
In 1969, JDR candidate J. Pompidou was elected president of France, and in 1974, after his death, the leader of the center-right party National Federation of Independent Republicans V. Giscard d'Estaing was elected. During their reign, the government was headed by the Gaullists (including J. Chirac in 1974-76). From the end 1960s a gradual shift away from dirigisme began, a number of social reforms were carried out aimed at meeting the demands put forward during the crisis of 1968. In the area foreign policy France continued to pursue an independent line, which, however, was distinguished by less rigidity and greater realism. Relations with the United States normalized. With the lifting of the veto on Britain's accession to the EU (1971), France's efforts to expand European integration intensified. Soviet-French relations continued to develop; France maintained its focus on détente and strengthening security in Europe.
The first “oil shock” of 1973-74 reversed the trend of accelerated economic development in France; the second (1981) - the “trend of power”: it passed from the right, in whose hands it had been since 1958, to the socialists. In the modern history of France, a modern period has arrived - a period of “coexistence”, political and economic instability, strengthening the position of business, and gradual modernization of society.
Government and political system of France
France is an indivisible, secular, democratic and social state with a republican form of government. Administratively, France is divided into 22 regions, 96 departments, 36,565 communes. The largest cities are Paris, Lyon (1.3 million), Lille (1.0 million), Nice (0.8 million), Toulouse (0.8 million), Bordeaux (0.7 million).
The Constitution is in force, adopted by referendum in 1958, with amendments in 1962 (on the issue of electing the president), 1992, 1996, 2000 (in connection with the signing of the Maastricht, Amsterdam and Nice treaties, respectively) and 1993 (on the issue of immigration).
The form of government since 1958 has been a semi-presidential republic: the Constitution clearly outlines the principle of priority of the president, who is not responsible to parliament, but is not the head of government. Since 1995, the President of France has been J. Chirac (re-elected in 2002), a representative of the center-right party “Union for the Unity of the People” (SON), heir to the Gaullist parties.
In the French political system, the president is a key figure. The President is elected for a 5-year term on a majority basis by direct universal suffrage (all citizens have the right to vote upon reaching the age of 18).
The main function of the president is to monitor compliance with the Constitution, performing the role of a national arbiter, ensuring the regular and proper functioning of the executive branch and the continuity of the state. The President is the guarantor of national independence and territorial integrity, France's compliance with its international obligations, he is the supreme commander in chief, represents the country in the international arena, and appoints senior civilian and military officials. Appoints the Prime Minister, forms a cabinet together with him and terminates the latter’s powers upon his resignation. The President presides over cabinet meetings and approves its decisions.
The president is elected independently of parliament and has the right to dissolve it with the obligatory condition of announcing the date of early elections. The president is deprived of the right of legislative initiative, but can issue decrees and decrees that have the force of laws, and organize referendums on issues of domestic and foreign policy. The President enjoys the right of suspensive veto on parliamentary decisions. Finally, the Constitution grants the president emergency powers when there is a “serious and imminent threat” to the territorial integrity of the country and a disruption to the “normal activities of public authorities.” In general, presidential power in France is comprehensive and has no definite boundaries.
The prime minister is appointed by the president for an indefinite term from among the deputies of the party that received the majority in the elections. In 2002, this post was taken by J.-P. Raffarin. The Prime Minister is responsible to both the President and Parliament. He directs the activities of the government and is responsible for it, ensures the implementation of laws, and is responsible for the defense capability of the country. If necessary, instead of the president, he conducts meetings of the Supreme National Defense Council, as well as in exceptional cases, meetings of the Council of Ministers (if there are special powers from the president in a particular area). The prime minister, together with the president, participates in developing the government's economic program if they belong to different parties (otherwise it is the president's mission).
The Prime Minister enjoys the right of legislative initiative: he and members of the cabinet can issue by-laws on economic and social issues. Approximately 20% of the bills considered by parliament are developed by the government, and the overwhelming majority of them (4/5 or more) are adopted.
The French parliament consists of two chambers - the National Assembly and the Senate. Deputies of the National Assembly are elected on a majority basis by direct, universal, equal and secret ballot for a 5-year term. Since 1986, the number of deputies of the National Assembly is 577 (previously 491). There is 1 deputy mandate per 100 thousand voters. Parties whose candidates overcome the 5% threshold in all 96 departments enter parliament. Members of parliament do not have the right to hold positions in the executive branch. A normal annual parliamentary session lasts at least 120 days. It is possible to convene an emergency session at the request of the Prime Minister or a majority of members of the National Assembly to discuss issues of special national importance; its opening and closing is carried out by special decree of the president of the country. At the parliamentary elections of 2002, the 12th Legislature of the National Assembly was elected as follows: SON 355 seats, French Socialist Party (FSP) 140, Union for the Defense of Democracy (UPD) 29, FCP 21, Radical Party 7, Greens 3, others 22 .
Chairman of the National Assembly - R. Forney (SON). The chairman, representing the parliamentary majority, is elected for the term of the legislature. Its main task is to ensure the normal functioning of the lower chamber. 6 of his deputies are heads of leading parliamentary parties. The agenda of parliamentary meetings is determined by the government, which thereby controls the current activities of the National Assembly.
Sphere legislative activity The National Assembly is enshrined in the Constitution and is limited to 12 areas (including ensuring civil rights and freedoms of citizens; basic issues of civil and criminal law; national defense; foreign policy; legal regulation property relations; nationalization and privatization, taxation and money issue and, of course, budget approval). Review and approval of the budget is the main ability of parliament to control the activities of the government; Moreover, deputies are prohibited from making proposals leading to an increase in budget expenditures. Lawmaking is carried out within the framework of 6 standing committees (the number established by the Constitution). They include 60-120 deputies; They are invariably chaired by representatives of pro-government parties.
The National Assembly has the right to seek the resignation of the government. The procedure is as follows: when rejecting a government program as a whole or a separate bill, the government raises a question of confidence; in response, the lower house is empowered to adopt a special resolution of censure. With the support of at least 50% of deputies, the cabinet is obliged to resign. However, the president has the right, having accepted the resignation of the prime minister, to immediately reappoint him to this post. Or, on the contrary, remove the prime minister, despite the support of the majority of parliamentarians.
The upper house of parliament - the Senate (317 members) is elected by two-stage voting and is renewed by a third every 3 years. The structure of the Senate is identical to that of the National Assembly. The Senate, unlike the lower house, cannot shut down the government; In relation to laws adopted by the National Assembly, the Senate has the right of suspensive veto. Composition of the Senate as of May 2003: SON 83 mandates, FSP 68, Union of Centrists 37, Liberal Democrats 35, Union of Democrats for Socialism and Europe 16, FCP 16, other 66 mandates.
Based on the Constitution of 1958, a quasi-judicial body was created in France - the Constitutional Council. It reviews acts issued by the legislative and executive branches of government for their compliance with the Constitution. The Council has 9 members. The president of the country, the heads of the National Assembly and the Senate (3 members each) have the right to nominate them. The appointment is for a nine-year term and cannot be repeated. The Chairman of the Council is appointed by the President of France from among the Council members.
Since 1982, local executive power has been elected (previously it was exercised by prefects appointed by the prime minister). At the departmental level, the elected bodies are general councils, at the regional level - regional councils.
France has a democratic and multi-party system. Valid approx. 25 games; 16 of them participated in the 2002 elections. However, only 3-4 parties have a real influence on political life. This is primarily the center-right Union in Support of the Republic (OPR), transformed into SON in 2002, and the center-left FSP. In con. 1980s The far-right National Front (NF) entered the category of major parties. In the 1990s. There was a strengthening of tripartism, associated mainly with the growth of the electoral successes of the NF against the backdrop of the stabilization of the right center and the weakening of the socialists.
The OPR, which emerged in 1976 as the successor to the South Democratic Republic, in foreign policy continued the Gaullist tradition of the “special path” of France - a great power and an international mediator. In the 1990s. with the complication of relations between industrial and developing countries, with the liquidation of the Soviet bloc, the need for French mediation sharply decreased; the rudiments of Gaullism remained in the form of France’s “special approach” to almost all problems of world politics and European construction. In the economic sphere, the OPR, unlike the center-right parties of other industrial countries, has not switched to neoliberalism. The position of the OPR on major economic issues (the role of the state in the economy, attitude towards business, the fight against unemployment) before the 2002 presidential and parliamentary elections was reminiscent of the views of European Social Democrats. From the beginning 1980s in presidential and parliamentary elections, the OPR consistently gained 20-22% of the votes. In the 1st round of the 2002 presidential elections, the candidate from the OPR, J. Chirac, received 19.7%, overtaking the leader of the FN, J.-M. Le Pen, by only 2%.
In the face of the threat of victory for the NF, the OPR set the task of uniting the center-right forces. The movement created around her, the Rally in Support of the President, became an important factor in the victory of the center-right in the elections (in the 2nd round, J. Chirac received 81.96%). Subsequently, the movement was transformed into SON, whose leader was the famous OPR figure Alain Juppe. The SON economic program, while still not openly proclaiming the principles of neoliberalism, provides for a reduction in the functions of the state and increased support for business. In the political sphere, SON aims to preserve and maintain the role of a great power, the leader of European politics (this was manifested in the position of France during the war in Iraq in 2003).
The second main party in France, the FSP, formed in 1971 on the basis of the SFIO, sees its task as the gradual transformation of society in the direction of socialism while maintaining a market economy. In the 2002 presidential elections, the FSP was defeated; its candidate, Prime Minister L. Jospin, gained only 16.2% of the votes and did not make it to the 2nd round. The defeat of 2002 continued the failures of the socialists, which began in the middle. 1980s and caused by their sharp shift to the right. In 1972, the FSP, which was in deep opposition, put forward the slogan of a “break with capitalism” through large-scale nationalization, the introduction of directive planning, “fair distribution” of income through radical tax reform, etc. With this program, the FSP and its leader F. Mitterrand won a landslide victory in the presidential and parliamentary elections of 1981. However, a significant deterioration in the economic situation caused by the implementation of measures to “break with capitalism” forced the FSP to turn to practice, and then to theories from the arsenal of the right . In the next program of the socialists (1991), society was no longer offered a “non-capitalist path of development,” but just another model of economic management. As a result, the FSP began to quickly lose the electorate, which shook its position of power. The powers of the socialists were full-scale only in 1981-86 and 1988-93, and in other years they were limited to either the executive or the legislative branch, which led to the coexistence, respectively, of either a left-wing president with right-wing governments (1986-88, 1993-95), either a right-wing president with a left-wing government (1997-2002), or to the complete transfer of power into the hands of the right (1995-97). In the 1990s - early. 2000s the socialists lost all elections - from municipal to European (except for the parliamentary 1997).
Constant defeats weakened the function of the FSP as a “bearing element” of the party structure and, as a consequence, the position of the entire left group of the French party system, already complicated by the sharp deterioration in the position of the communists. Until the beginning 1990s The PCF managed to maintain a stable 8-10% electorate. But then it shrank: to one part of the voters the positions of the PCF seemed too traditional and dogmatic, to the other, the largest part, not radical enough. In the 2002 presidential elections, only 3.4% of voters voted for the General Secretary of the PCF R.Yu. The PCF, which has finally lost its position as a significant political force, lags behind the extreme left parties in popularity, whose leaders in the 1st round of the 2002 presidential elections collectively gained 11.2% of the votes (including Labor - 5.7%, Communist revolutionary league - 4.3%). The total percentage of supporters of the FSP and FKP in 1981-2002 decreased from 37 to 19.6%.
The loss of positions by traditional left parties is largely due to profound changes in French society: the transition to the post-industrial stage of development, the growth of educational levels, the elimination of the most glaring forms of inequality, the erosion of former large social groups and their political subcultures, the passing into the past of generations that considered class as the central problem. confrontation, presidential or parliamentary versions of the republican system. All this leads to an increase in voting not based on social affiliation, but on the basis of personal political preferences and interests. Hence the emergence of multiple small parties and the fragmentation of the electorate.
In modern France, a situation has arisen where the small number of supporters of the newest world social projects (neoliberalism, modernization, integration) does not allow the formation of a large party in their support. On the contrary, a significant segment of voters, demanding changes, understands them as a backward movement, a kind of counter-reformation. The most consistent and active opponents of neoliberalism and integration are the electorate of right-wing and left-wing extremist parties: 1/3 of the French voting.
The rise to power of the far-right National Front began in 1974 (0.9% in presidential elections). For a long time the NF did not seem to be a significant political force. Its importance began to grow rapidly in the 1990s, when France was gripped by a deep and protracted economic crisis.
The ideological constructs of SF are very primitive. The long-term deterioration of the French economy is explained by the influx of immigrants occupying jobs and the conspiracy of large foreign capital and “Brussels technocrats” who are alien to the interests of France. The proposed recipes are strengthening presidential power and security forces, stopping immigration, leaving the EU, including abandoning the euro.
The NF is not yet able to transform an increase in electoral influence into an increase in political influence. The majoritarian electoral system and the refusal of the central organizations of the OPR and the FSP from electoral agreements with the NF have so far contributed to the fairly successful repulsion of attempts by the far right to penetrate various government bodies, incl. to the National Assembly. Therefore, the third main party of France is so far “a force without power”, which does not influence domestic and foreign policy.
Modern France is characterized by a relatively low importance of trade unions. The trade union movement, like the party movement, is distinguished by the multiplicity of organizations that form it. The main ones are: the General Confederation of Labor (CGT), traditionally close to the PCF; the socialist-oriented French Democratic Confederation of Labor (FDCT), the independent CGT-Force Ouvrier and the General Confederation of Personnel. The French trade unions, formerly truly mass organizations that united St. 30% of wage earners now claim 1.5 million members (10% of the wage labor force). However, of this number, the overwhelming majority are functionaries working for hire (for example, in the FDKT - 810 thousand out of 865 thousand declared members).
Among business associations, the largest is the Movement of French Companies (Medef), which groups 750 thousand companies. Medef takes an active part in the development of economic policy, gives recommendations to the government on foreign economic issues, and, along with trade unions, participates in regulating the labor market and in managing the social sphere.
Domestic policy since the 1980s. was characterized by significant instability. In conditions when the 2 main ruling parties offered society diametrically opposed options for social structure and development models, the course directly depended on the party affiliation of the prime minister and changed dramatically with his change. When this post was occupied by socialists, domestic policy had a pronounced social orientation and redistributive character; these features were lost when representatives of the government were at the head of the government, seeking to support business by reducing redistribution. The frequent change of ruling parties at the helm of the board deprived both the OPR and the FSP of the opportunity to complete the reforms started by each of them, which negatively affected the state of the economy. The course was more consistent in other areas of public life, where the reforms carried out were not canceled with the change of government. So, in the 1980-90s. has been cancelled the death penalty; an administrative reform was carried out, uniting 96 departments into 22 larger regions; The powers of local authorities have been expanded. In the social sphere, there were: a reduction in the retirement age from 63 to 60 years, an increase in the duration of vacations to 5 weeks, a reduction in the working week from 40 to 39, and then to 35 hours, expansion of trade union rights, etc.
One of the main directions of the domestic policy of the government of J.-P. Raffarin is the fight against crime, which really increased noticeably in the 1990s. with the worsening economic situation and rising unemployment, especially among immigrants. Reducing the crime rate was the central slogan of the election campaign of J. Chirac, who in this regard insisted on the need to strengthen the relevant security forces. In the 2nd half. In 2002, police reform was carried out: its staff was expanded (which was at the level of 1945 - with a 20 million population growth) and the powers of police officers were expanded. Another direction of domestic policy is administrative reform, which provides for decentralization and giving greater independence to local authorities.
The main direction of French foreign policy in the last quarter of the 20th century. 21st century European construction appeared. The creation of a Common Economic Space, common political power, and a joint defense system is invariably proclaimed as the main goals of all presidents and all governments. France supported all measures to unite Europe: the Schengen Agreement of 1990, the Maastricht Treaty (although only 50.8% of voters voted in its favor at the national referendum), the Amsterdam (1997) and Nice (2000) treaties. She supported the entry into the EU of Greece, Spain and Portugal and a new stage of expansion in the Eastern European direction, scheduled for 2004, although with reservations regarding the distribution of agricultural subsidies.
The foreign policy course of France is characterized by constant anti-Atlanticism, especially clearly expressed in the position of Charles de Gaulle, which became muted after his departure, but did not completely disappear. France constantly contrasts its position with the American one on almost all issues of international life. The latest example was France's attitude towards American actions in Iraq, which caused another deterioration in Franco-American relations.
From ser. 1990s There have been changes in relations with developing countries, expressed in the refusal to maintain priority zones of strategic influence in the former colonies and in a more global approach, providing for the reorientation of assistance towards the poorest countries, regardless of their former colonial affiliation.
Having been a member of NATO since its founding, France left the military organization in 1966. It has not returned to it until now, although in 1995 it again became a member of the NATO Defense Committee, and in 1999 it participated in the operation in Kosovo. This return is becoming increasingly problematic given France's desire to create independent Armed Forces EU.
The French Armed Forces include the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Corps of Gendarmes. The number of Armed Forces is 390 thousand people. (including Navy 63 thousand people and Air Force 83 thousand people). The transition to a professional army (since 2000) was carried out as part of the military reform carried out since 1996, the completion of which is scheduled for 2015. Its main tasks are the revision of military doctrine with a shift in emphasis to rapid response to suppress hotbeds of conflict anywhere in the world, increasing the effectiveness of the armed forces reducing their number to approximately 300 thousand people, as well as reducing military spending. Their share in the state budget for 1992-2002 decreased from 3.4 to 2.57%, while maintaining and even expanding funding for priority programs in the region the latest weapons. In terms of military spending, France is noticeably superior to Germany, Great Britain, and Italy. France also has higher expenditures on military R&D and arms purchases (28% of military expenditures in the 2002 budget).
France is one of the most powerful military powers in the world. Its military-industrial complex provides the national armed forces with modern types of weapons, and also exports them widely abroad. In 2002, France ranked 3rd in the world in exports of conventional weapons. France is a nuclear power; its army has 348 nuclear warheads. They are equipped with land-based aircraft and aircraft of the Charles de Gaulle aircraft carrier, as well as 2 submarines (the third is planned to be launched in 2004).
France has diplomatic relations with Russian Federation. France recognized the USSR on October 28, 1924.
Economy of France
Economic evolution of France in the 2nd half. 20th century was distinguished by an unusually wide scale of state activity. This intervention, which allowed France to overcome its historical lag in the economic sphere, until the middle. 1960s was relatively effective. But subsequently, attempts to expand the participation of the state in production, to preserve the “redistributive economy” and the “welfare state” were an anachronism, which led to the deterioration of the state of the French economy and a decrease in the dynamics of its development. With the transfer of executive and legislative power to the center-right, liberalization reforms began in the economic and social sphere.
France's GDP is 1520 trillion euros (2002). France ranks fourth in terms of share in global GDP and exports. However, the share of F. in the GDP and exports of developed countries in the 1980-90s. decreased: respectively from 6.9 to 6.04%, and from 8.86 to 8.11%. Per capita GDP 25.50 thousand euros (2002). Unemployment 9.1%, annual increase in consumer prices 1.8% (2002).
Economic growth 1980s - early 2000s characterized by unevenness. Main macro indicators grew slowly at the beginning of both decades, especially in 1991-95; favorable conditions developed in the 2nd half. 1980s and in 1996-2001. A new decline was noted in 2002 and was largely due to a decrease in global demand and rising energy prices. A way out of the crisis was outlined in mid. 2003.
Shifts in GDP by production consisted of a decrease in the importance of agriculture and industry while increasing the services sector. The share of the agricultural sector decreased in 1980-2002 from 3.7 to 3.1%, industry, including construction, from 42.0 to 26.4%. Accordingly, services increased from 54.3 to 70.5%. The current structure of GDP in terms of production is fully consistent with similar proportions in other developed countries. This also applies to the French employment structure, where changes have followed similar directions. During this period, the proportions of employment were redistributed from agriculture and industry with construction (a drop from 8.7 to 4.5% and from 34.2 to 23.1%, respectively) to the service sector (an increase from 57.1 to 72.4% ).
French industry (without construction) accounts for 22.2% of GDP, 3.93 million employed, 20% of total investment, 94% of merchandise exports, 1/3 of direct foreign investment. Quite sluggish development of this area in the 1980s - mid. 90s in the last five years of the 20th century. gave way to rapid growth (3.8% on average annually). Investments grew by 7-8%, incl. in intangible assets (training of specialists, R&D, purchase of computer programs, advertising) - by 10-12% per year. The acceleration was facilitated by good global conditions, increased domestic demand due to the dissolution of unemployment, and a general improvement in the position of French private business, which strengthened by the end of the century. The low exchange rate of the franc during the transition to a single euro currency played an important role. French industry survived the 1997-98 crisis without damage. The reaction to the early crisis was worse. 21st century: in 2001, production growth was only 0.6%, in 2002 - 1.6%.
In the 1980-90s. deep structural transformations continued in industry, consisting of concentrating efforts on several advanced industries - automobile manufacturing, production of telecommunications equipment, pharmaceuticals and perfumes, aerospace engineering, nuclear energy. The total share of these 5 industries in industrial turnover is 43.8%.
The leading position is occupied by the automotive industry (17.7% of general industrial turnover). From the end 1980s annual car production remains stable at 3 million units. (2002 - 3,100 million, 5.4% of world production, 20.3% of Western European production). Export of cars is 42.6% of the total volume of their production. 99% of the industry's production belongs to 2 groups - Peugeot-Citroen and Renault. They approximately equally control over 60% of the national market and 23.8% of the Western European market, where they are still noticeably inferior to German manufacturers.
In 2nd place in terms of production volume are pharmaceuticals and perfumes (in total industrial turnover 13.2%). In terms of the cost of manufactured pharmaceuticals, France ranks 4th in the world, and in terms of their per capita consumption - 3rd (after the USA and Japan). Export industry 30% of production. The main producers are the Rhone-Poulenc concerns (6th place in the world), Elf-Atosh and Air Liquide.
Paris is the recognized perfume capital of the world, where such famous manufacturers of expensive cosmetics as Chanel, Ricci, and Saint Laurent operate. More mass-produced products are produced by L'Oreal - 13% of the world's perfume turnover, 1st place in the world. French perfumers export 38.5% of their products abroad.
Electrical and electronic engineering is quite a bit inferior to pharmaceuticals and perfumery (13.0% of general industrial turnover). More than 1/2 of the industry's products (54.6%) are office equipment and computers, long-distance communication equipment and electronic components. 48.8% of products are exported (including 59.8% of electronic components). The main manufacturer, the Alcatel concern, is one of the top three global manufacturers of telecommunications equipment. It accounts for 39.6% of the national industry market; for the Thomson group (the world's second largest manufacturer of military electronic equipment) - 23%.
In the field of aerospace production, France is a recognized Western European leader. The Aerospatiale company is one of the leading participants in the Airbus Industry European consortium (the main supplier of civil aircraft to the European market), where it owns 37.9% of the shares. It also owns a 70% stake in the Eurocopter association (1st place in the world in the production of civilian and 2nd place in military helicopters). The Arianespace concern controls approximately half of the global market for commercial launches of artificial Earth satellites.
In the last decades of the 20th century. Nuclear energy has become the basis of the French energy industry, now accounting for 10.5% of total industrial turnover. This was facilitated by the presence of its own large reserves of uranium. With the growth of primary energy consumption in 1980-2002 from 56 to 134 million tons of standard fuel, the share of nuclear power plants in it constantly grew: in 1980-2002 from 6.6 to 38% of national consumption. The share of other energy carriers over these years either decreased (coal from 18.1 to 4%, oil products from 54.4 to 36%, hydropower from 8.6 to 3%) or grew slightly (gas from 7 to 14%, alternative types of energy - up to 7%). In 2002, nuclear power plants generated 77% of electricity (1st place in the world).
As in other developed countries, the transition to the post-industrial stage of development was accompanied in France by a further decline in the share of agriculture in the main national economic structures. The share of food in national exports has also decreased (9.6% in 2002). In absolute terms, agricultural production increased by 87% during this period. And although French politicians no longer aim to turn the country into the “breadbasket of Europe”, as in the time of de Gaulle, France accounts for 23.7% of Western Europe’s agricultural production (1st place in the EU).
In the 1980-90s. The process of concentration continued in the industry. France has traditionally, since Napoleonic times, been a country of small farms with fragmented land ownership. Although the average farm area has almost doubled compared to the beginning. 1980s (42 and 23 hectares, respectively), 49% of farms are small and tiny (including 29.1% with an area of less than 5 hectares). Only 1/3 of farms own agricultural areas of 50 hectares and above (including 12.2% from 100 hectares). It is these large landowners who provide 75.7% of agricultural production.
An important factor in the development of agricultural production is the growth of technical equipment. From the end 1980s the number of tractors in the French agricultural sector has decreased, but mainly due to less powerful ones (up to 80 hp), while the share of more powerful ones has increased from 16.2 to 33.8%. Many other machines and mechanisms are actively used. The industry is completely electrified.
Unlike most other European countries, whose agriculture is focused on livestock, the French agricultural sector is multidisciplinary. Crop production, which is considered the main activity of 39.8% of farms, occupies half of the arable area and provides 48.9% of the total value of agricultural products. Its traditional specialization is the production of soft wheat. France is one of the great grain powers of the modern world (3rd place among developed countries and 1st in Western Europe, half of Western European grain exports). Wheat accounts for 64% of the production of cultivated grains (55% - soft). In terms of wheat exports, France ranks 2nd-3rd in the world (with Canada after the USA).
Other grain crops include oats, barley, rye, and corn. Viticulture, oilseed production, horticulture and gardening play an important role. 13.9% of farms operate in viticulture. 2.9% of arable land is occupied by vineyards, but this industry produces 28.5% of agricultural products. France is the world's main wine producer (shares 1st-2nd place in the world with Italy). Production volume 62.93 million hectoliters (2002). More than a thousand varieties of wine are produced, 1/4 of which are vintage. OK. 20% of wines are exported. The oilseeds sector provides 6.3% of agricultural output. France accounts for 39.2% of European oilseed production. Vegetable and horticultural products account for 10.5% of the total value of agricultural products. In terms of average per capita consumption of vegetables, France is the leader in the modern world. It ranks 2nd in the world in apple harvesting, 1st-2nd in Western Europe in apricot and pear harvests.
Livestock farming accounts for 51.1% of the value of agricultural products, incl. cattle breeding - 16.1%. In terms of its livestock, France ranks 1st in Western Europe and 6th in the world (20.3 million heads). This is approximately 1/4 of the EU population. France also accounts for 10% of the EU's sheep population and 12.9% of its pig population (15.93 and 9.32 million heads, respectively). It is the leading European meat producer and is among the top five global meat producers (3,755 million tons in 2002). Dairy farming is also developed (18% of the value of agricultural products). France is the world's 2nd producer of cheeses (over 2 million tons) and butter, the 2nd EU country in the production of whole milk products. Poultry farming is developing well: here too, France is 2nd in the world after the USA and 1st in Europe.
France is one of the most powerful transport powers in the world. Road and air transportation, as well as rail transport, have reached a high level. These industries account for 7.3% of GDP and 7.9% of employment. In 2002, the total volume of land transport reached 215.3 billion tkm; 79% of it (169.8 billion) was carried by road transport. France has a dense network of roads with artificial turf (1.1 million km - 2nd place in the world after the USA). In terms of the quality of the road surface and the availability of signage, French roads in continental Europe are comparable, perhaps, only to German ones. Cargo is transported by 9.2 million trucks, 10% of transportation is combined.
The length of railways reached its maximum in the 1930s. and then decreased (2002 - 32 thousand km). Freight turnover is 50.4 billion tkm. Passenger transportation 48.9 billion passengers/km. 2/3 of their volume in terms of the number of passengers falls on the Paris hub. Its exclusive dominance over a highly centralized railway network has been a characteristic feature of French railway construction since the 19th century.
French railways are actively electrifying. The length of electrified lines is 13,570 km. High-speed transport (350 km/h) is widely available. France is one of the world leaders in its development and implementation. The first high-speed line was opened in 1981 between Paris and Lyon. Now such lines connect the capital with Marseille, Strasbourg, Nice, La Rochelle, as well as Brussels and London (Channel Tunnel). In the future, there is an extension of the line to Brussels to Amsterdam and Cologne, the La Rochelle line to Bordeaux, and the Lyon line to the territory of Italy and Switzerland.
In 2002, 79.6 million passengers and 1.9 million tons of cargo were transported by air. The bulk of transportation occurs at the Paris complex, where 2 operate major airports: Roissy-Charles de Gaulle and Orly (together 67.3% of all national domestic and international passengers and 89% freight transport). Le Bourget, formerly the capital's main airport, now serves only business aviation. Regional airports - Nice, Satolya (Lyon) and Toulouse - together transport 19.7 million passengers per year, 6.3% of the national cargo volume.
Meaning water transport in domestic and external transportation is small. Merchant fleet tonnage is 4.5 million tons. France has 89 seaports with a total cargo turnover of 300 million tons. 90% of it falls on 6 ports, incl. 48% - to Marseille and Le Havre (113 and 47.4 million tons, respectively); the remaining traffic goes through Dunkirk, Calais, Rouen and Bordeaux. The length of inland shipping routes is 8.5 thousand km, but only 5.5 thousand are used. The freight turnover of river transport is 181.6 billion tkm (2001).
1990s became a period of exceptionally rapid development of the communications sector (more precisely, information and communication services); in 1996-2000 the average annual increase in its production was 20%. The growth was combined with huge qualitative shifts, which made it possible not only to eliminate the long-term lag in the field of telephone installation from other Western countries, but also create to the beginning. 21st century one of the most modern electronic digital communication systems in Europe. The shifts were primarily due to the rapid expansion of mobile telephony and the increase in the number of Internet users. For 2001-02 the number of subscribers mobile communications increased from 31 to 37.3 million. This represents 62.5% of the population - still less than in the UK, Italy, Spain, and Scandinavian countries, but more than in the USA (50%).
In 1997, there were 500 thousand Internet users in France, by the beginning. 2002 - already 19 million people, 31.9% of the population (among managers and people engaged in intellectual work - 73.1%, among students and students - 73.3%). Of the planetary number of World Wide Web users, France accounted for 4% by 2002.
Trade plays an important role in the French economy (13.0% of GDP, 13.4% of employment). Major change since the 1980s. - transition from small retail to integrated organization, to modern complexes: super and hypermarkets. A supermarket in France is considered to be a store retail space 400-2500 m2, a hypermarket - from 2500 m2, more than 1/3 of the turnover of which comes from trade in food products (as opposed to a “large store” with a similar area, but selling mainly manufactured goods). In the beginning. 1980s the share of integrated trade accounted for 27% of retail turnover, in 2002 - 51.4%. In 1986-95, 350-450 super- and hypermarkets were opened in the country annually, in 1996-97 - up to 200, and in 1998-2002 - up to 100. According to this indicator, France is one of the first places in the EU, trailing only Finland, Ireland and Denmark. Now the market share of integrated trade is 66.7% for food and 20.4% for manufactured goods. In the latter area, specialized (non-food) stores dominate, although their share is gradually decreasing (only for 1995-2002 - from 41.9 to 40.4%).
France continues to be a classic country of small trade. Retail outlets with an area of up to 40 m2, mainly selling food, account for at least 20% of the industry's enterprises. But their number is decreasing (in 1995-2002 by an average of 6% per year), and the market share is falling (from 28.5 to 24.1%).
During 1980-2002, the French economy experienced a sharp increase in the share of the service sector. The dynamics of services between 1980-2002 exceeded the rate of economic growth by 1.2 times. Services to enterprises developed especially quickly (+5.2% on average annually). The main part of this area is market services, incl. 60% - services to enterprises. These are two groups: consulting, which includes at least a dozen types of activities (legal, advertising, accounting, engineering, marketing, information, etc.), etc. operational services - rental, personnel selection, security measures, etc. 244.3 thousand enterprises are employed in consulting, 92.5 thousand in operational services. It is clear that the main users of these services are companies (80% of consumption). But they are also large consumers of services to the population, especially those provided by travel agencies (57%), real estate firms (41%) and the hotel and restaurant sector (39%). The market for market services is growing mainly due to the expansion of their consumption by companies.
The credit and financial system is represented by the French Bank, 412 commercial banks and 531 financial companies. Since joining the eurozone, the Bank of France has played a limited role in monetary policy. Monetary gold reserves in 2001 amounted to 97.75 million troy ounces; the refinancing rate was 4.23%, interest rates on loans were 6.7%, on deposits - 2.63%. Banks are highly concentrated: the 8 largest of them account for 86% of loans issued and 74% of assets. As elsewhere in industrialized countries, in France there is an active process of universalization of banking and financial services, intensifying competition between various financial institutions.
France is the only large developed country where in the 1980-90s. Neither monetarist theory nor liberal economic practice were officially adopted. The economic policy of the socialists during their periods in power was based on Keynesian methods of regulation, i.e. on stimulating demand. The right demonstrated attempts to stimulate supply, although rather limited.
In economic policy con. 20th century There are several milestones that mark these opposing trends. The first was the nationalization of the beginning. 1980s, unprecedented for the post-war period. A third of industry, 2 leading financial holdings, 36 large banks, and many insurance companies were in the hands of the state. At the same time, active price and exchange controls and a strict tax on large fortunes were introduced.
Through huge budgetary injections, the socialists achieved the recovery of state-owned companies. But the state budget deficit increased sharply, and businesses began to massively curtail production in France. The forced transition of the socialists to a policy of austerity swung the pendulum of electoral preferences to the right - and the OPR, which won the parliamentary elections, attempted to turn the economy “face to the market”, which became the next milestone in economic policy. The privatization of state-owned companies and deregulation of the financial sector began (the abolition of controls over foreign exchange transactions, over the movement of capital, the removal of numerous restrictions on financial markets, the elimination of price controls). The socialists who seized power in 1988 did not return to nationalization and did not make any changes in the financial sector. However, they practically stopped privatization and again stimulated demand using the expenditure side of the state budget. The increased tax burden has become a serious factor in reducing the profitability of enterprises. The ineffectiveness of this policy, especially in the early crisis. 1990s, contributed to another transition of (legislative) power to OPR. Formed from its representatives, the governments of E. Balladur and then A. Juppé again tried to “shift the steering wheel” to the right. But in the context of the ongoing economic crisis, the right was again given only a three-year sentence. In 1997, with the victory of the Socialists in the parliamentary elections (the government of L. Jospin), a new milestone was outlined in economic policy: another long turn to the left.
Foreign observers called Jospin's economic policy dirigisme, although it looked like such mainly in comparison with the economic course of the Anglo-Saxon countries. The state no longer provided direct support to individual companies or industries; government regulation was formally aimed at improving the general economic climate; indirect levers of influence were more often used. Jospin carried out a very large privatization (180 billion francs) in order to bring the budget into line with the requirements of the Maastricht Treaty. However, France retained large state ownership and state control over the prices of natural monopolies, tariffs for health care services, the dynamics of rents and the prices of 80% of agricultural products that fall under the provisions of European pricing. Socialists continued to stimulate demand by redistributing national income in favor of wage labor.
Redistribution measures carried out under the slogan of “equalizing the income of labor and capital” included reducing taxes on the population and increasing them on companies. In 1997-98, additional fiscal payments were imposed on companies: social income tax, general tax on polluting industries and a corporate tax surcharge for firms with a turnover of St. 50 million francs (for almost everyone except small businesses), etc. The total increase reached 4.5 billion euros. At the same time, the fiscal pressure on the “rich” was increased individuals(additional taxation of income from transactions with securities, from savings, etc.), which included income recipients of the middle and upper groups.
Enormous amounts of tax revenue were used to improve the situation of low-income groups (in 2000-01 their tax payments decreased by 21 billion euros), as well as to expand employment by increasing jobs in the public sector (3 youth employment programs) and increasing labor market flexibility (reducing working week from 39 to 35 hours while maintaining unchanged wages in exchange for allowing previously prohibited overtime and Sunday work, night shifts, etc.). These measures, which coincided with an improvement in the global economic situation, had a positive effect: unemployment began to decline; the creation of 1 million jobs pushed up the movement of domestic demand and the dynamics of economic growth; the growth of tax revenues contributed to the reduction of the budget deficit, and the public debt decreased. But government policy worsened the situation of companies. Their level of taxation in France is still one of the highest in Europe: the corporate income tax rate is 42%, entrepreneurs pay 60% of total contributions to social funds (which is equal to 6% of GDP). The profitability of companies was at a low level - 15.6% even in the prosperous year 2000. The subsequent deterioration of the global market environment contributed to its further decline and, as a result, the stagnation of investments, the cessation of employment growth in the business sector, and then in the public sector of the economy, where employment programs exhausted. As a consequence of these processes, the volume of tax revenues to the budget decreased, the expenses of which remained at the same level. They could be reduced by reducing social items. The government tried to reduce spending on health care by tightening controls on public hospital spending, but backed down in the face of a huge wave of strikes by health workers. Likewise, the reform in the field of financing higher and secondary education failed. The pension reform, which had been debated for 5 years, was never started, the need for which was long overdue due to the progressive aging of the population. K con. In 2002, the state budget deficit reached 2.7% of GDP, which in 2003 increased to 4.0%, thereby exceeding the Maastricht maximum. The national debt also reached it (2003 - 61.2% of GDP).
The government of representatives of OPR (later SON) headed by J.-P. Raffarin, formed in June 2002, sees its primary task in the economic sphere in supporting entrepreneurship, which should help improve both the general economic and social situation (resolving unemployment through the creation new jobs in the business sector). In this regard, motivating his actions by the need to streamline the state budget, Raffarin curtailed government employment programs and began to change the taxation system. The first measure was a 5% reduction in income tax, which should be followed by an increase in the lower limit of the tax base for large fortunes. State-owned companies will be privatized, incl. natural monopolies. The government plans to begin reforming the healthcare and higher education systems in the near future and has already announced the start of pension reform, which includes increasing length of service and increasing contributions to pension funds.
The announced reforms cause extreme dissatisfaction among the population, who see them as a threat to their standard of living. In 2001 the average monthly wage full-time employment in the private and semi-public sector after tax deduction was 1,700 euros. Hourly wages for full-time workers were about 20% higher than for part-time workers. For management personnel and people with higher education, the average monthly salary was 2.6 times higher than for workers and employees; this gap has persisted since the beginning. 1990s Discrimination against women's labor is equally consistent: a woman in any position earns 25% less than a man. The income of the French also includes numerous and varied social benefits, which together provide on average at least 1/3 of an increase in wages.
In 2002, 16.7% of the population's income was allocated to savings, and 83.3% was spent. In the structure of consumer spending, 15.4% were expenses for housing maintenance and repairs, 12.9% for food, 9.6% for the purchase of clothing and footwear, 6.4% for durable consumer goods (incl. 2.9% - for cars). 6.3% each was spent on paying for electricity and healthcare services. The largest item of expenditure was leisure and telecommunications services (together 21.4%). More than 90% of families live in comfortable apartments or separate houses with all amenities. The same percentage of families own at least one car, almost 100% have a refrigerator, 67% have a freezer, 91% have a washing machine, 60% have a microwave oven, etc. Every 9th family owns country house or a dacha. Living conditions in rural areas differ little from urban ones.
Turn of the 20th-21st centuries. marked by a significant increase in the importance of the foreign economic sphere in economic life. The export quota in 2002 was 27.2%; 86% of exports and 79% of imports came from EU countries; 82.7% of exports are goods, incl. 69.7% - industrial products (machinery and equipment - 24.7%). At a fast pace from mid. 1990s the export of capital grew, in which France had previously lagged noticeably behind. In 2001, the total volume of foreign direct investment amounted to 197 billion euros. Accumulated foreign investments exceeded 500 billion euros in 2001 (1/10 of the world total).
Science and culture of France
France is one of the world's leading scientific powers. National R&D expenditure €30,545 million, or 2.14% of GDP (4th in the world) (2001). 314.5 thousand people are employed in science, 48.9% of them are teaching staff of universities, of which there are approx. 20 (including the oldest in Europe, Paris - the Sorbonne and the University of Montpellier, founded respectively in the 13th and 15th centuries). 160 thousand people are directly involved in scientific research and development. (75% in the private sector). They are concentrated in various research and development companies, laboratories and technical centers (there were 5,373 of these out of 2000). The state's share in financing scientific activities was 21.7% (2001); the funds received were directed mainly to fundamental research, as well as to such industries as nuclear energy, various space programs, weapons production, transport and communications. The business sector concentrates its efforts in applied research, mainly in electronics, general mechanical engineering, automotive industry, and the chemical industry. These industries accounted for 46.7% of patents issued to residents. However, despite the considerable amount of funds allocated to R&D, French scientific thought in the technical field lags behind its main foreign competitors. Of the 160.0 thousand patents registered in France in 2001, residents received only 21.6 thousand (13.5%); the balance of trade in patents and licenses is persistently negative. World famous names belong to the French, primarily in the social sciences: in sociology F. Durkheim, C. Lévi-Strauss, M. Foucault, A. Touraine, in history - F. Braudel.
It is unlikely that there is another country that has had as powerful an influence on Western and world culture in the last 3-4 centuries as F. Castles on the Loire, parks and palaces of Versailles, paintings by old masters from Clouet to Poussin, Greuze, Chardin, the romantics of Delacroix and Courbet, the Impressionists, the musical creations of Berlioz and Ravel are world-class masterpieces. Paris has been considered the cultural capital of the world almost since the time of Louis XIV. In the 20th century this tradition was continued. Here, in the interwar and post-war years, artists from all over the world lived and worked - the Spaniards Picasso and Dali, the Italian Modigliani and the Dutchman Mondrian, the French Marche, Signac, Léger, who together represented almost all the numerous directions of modern painting; France is the birthplace of modern abstract art and, along with the USA, op art and pop art.
French literature, the first written monument of which dates back to 842, has always been one of the largest phenomena in world literature. The medieval tradition of literary creativity (The Song of Roland, works of troubadours and trouvères, city fabliaux, poems by F. Villon) was continued in the 16th century. poets of the Pleiades, Rabelais and Montaigne, in the 17th century. - Racine, Corneille, Moliere, Lafontaine, in the 18th century. - Voltaire, Beaumarchais, encyclopedists. In the 19th century French literature was adorned by such great names as Hugo and Balzac, Stendhal and Flaubert, Zola and Maupassant, in the beginning. 20th century - M. Proust. In France, in the interwar years, the literary and philosophical movement of existentialism - the philosophy of existence (J.-P. Sartre, A. Camus, Simone de Beauvoir) arose. In the post-war period, the “family” and historical novels of F. Eria, E. Bazin, M. Druon became brilliant examples of critical realism. The creators of the “new novel” direction were A. Robbe-Grillet and Nathalie Sarraute. The names A. Maurois, M. Eme, B. Viana are well known. Writers A. Gide, F. Mauriac, Saint-John Perse are Nobel Prize laureates in literature.
French cinematography is very popular in the world. The works of directors M. Carne, C. Christian-Jacques, R. Clair, R. Vadim starred such stars as J. Gabin, J. Philip, Bourville, Fernandel, L. de Funes, B. Bardot. French cinema is known primarily for the names of L. Besson, P. Richard, J. Depardieu, Annie Girardot. The undying tradition of French chanson after World War II was continued by Edith Piaf, Yves Montand, C. Aznavour, Dalida, J. Brel, Brassance, S. Adamo, Mireille Mathieu and others.
POPULATION - 58.3 million people, mostly French. About 5 million people are foreigners, mostly Africans.
GEOGRAPHY - State in Western Europe. In the northeast it borders with Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany, in the east - with Germany, Switzerland, in the southeast - with Monaco and Italy, in the southwest - with Spain and Andorra. France is washed by the North and Mediterranean Seas, the Pas de Calais, the English Channel and the Bay of Biscay. The total area is 551 thousand sq. km.
CLIMATE - Summer is quite hot (in July-August from +20 C to +25 C), winter is mild (in January from 0 C to +3 C), it rarely snows. The ideal time for tourism is spring and early autumn.
LANGUAGE - State French. In the outskirts of the country they speak Basque, Catalan, dialects of Italian, German, Flemish and Breton.
CURRENCY - French franc (FRF) = 100 centimes. Banknotes in circulation are in denominations of 500, 200, 100, 50 and 20 francs. And coins of 10, 5, 2, 1 franc, 50, 20, 10 and 5 centimes.
RELIGION - about 48% Catholics, 15% Protestants, 1.3% Jews and 4.5% Muslims.
POLITICAL STATE - independent republic with a presidential form of government. The highest legislative power belongs to the bicameral parliament. France includes "overseas departments" - Guadeloupe, Martinique, Guiana, Reunion, Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, N. Caledonia, French Polynesia, etc.
 TIME - 2 hours behind Moscow.
TIME - 2 hours behind Moscow.
MAIN ATTRACTIONS - The cultural center is certainly Paris, which houses the main museums of the country - the Louvre, the Pompidou art center, the Grand Palais ( Grand Palace), Picasso Museum, Rodin Museum, D'Orsay Museum of Painting, Birges, Temple, National Museum of the Middle Ages (Thermes of Cluny), Museums of Impressionism and Orangerie in the Tuileries Garden, Les Invalides with cathedrals and Napoleon's tomb, Champs de Mars, Pantheon, Luxembourg Gardens, Bois de Boulogne with a wonderful rose garden, Sorbonne, Madeleine Church, Place de la Concorde, Opera theatre, Museum of the History of Paris (Carnavalet), Wine Museum. In addition, in Paris there are such architectural masterpieces as the Eiffel Tower, Notre Dame de Paris Cathedral, the Sainte-Chapelle Church, the Arc de Triomphe, the Palais Royal, the Elysee Palace, the monumental city of Versailles, the University, and the Latin Quarter. As well as Montmartre, Champs Elysees, Bois de Boulogne, popular among tourists, Botanical Garden, the zoo and the world famous cabarets: Moulin Rouge, Crazy Horse and Paradis La Tène. Near Paris is EuroDisneyland, Europe's largest amusement park. In Cannes, not far from Nice, there are the Loire Castles, which are of great historical value. In the city of Biarritz, on the shores of the Bay of Biscay - "Villa Eugenie", museums - the sea, miniature cars, chocolate, a lighthouse and the Virgin Rock. The Nimes-Garon department has many monuments from the Roman era - circuses, viaducts and villas. The series is famous throughout the world magnificent resorts Cote d'Azur(Rivieras) - Grasse, Saint-Tropez, Villefranche-sur-Mer, Juan-les-Pins, Golfe-Juan, Saint-Raphael, etc. Cannes (Cannes): Palace of Festivals and Avenue of Stars, Red Staircase, Avenue of Liberty and Fortress -12th century museum on the Suquet hill, Star Beach and the Bay of Cannes. Nice: Promenade des Anglais, Building of the famous Opera of Nice, Saint-Reparat Cathedral, Chapel of Mercy, Chateau Hill with a castle, a beautiful park and a waterfall, Museum of Modern Art, Museums of Dufy, Matisse, Marc Chagall, Museum of Art and History, Russian Church, Palace Congress Akropolis, Palace of Justice. Antibes: Grimaldi Castle built in the 12th century, Picasso Museum. The French Alps are the most high mountains Western Europe, the world's largest center winter sports. Popular resorts- Chamonix and Courchevel, Val d'Isère and Tignes in Val Thorens, Les Deux Alpes, La Pland, Megève, Meribel, etc.
ENTRY RULES - France is part of the Schengen zone. You must have a visa obtained on the basis of an invitation, a foreign passport, and insurance for at least $30,000. Children traveling with one of the parents must have a copy of the birth certificate, a power of attorney from the other parent for the child to travel in Russian and French, certified by a notary. When entering France, they may require a return ticket; according to French law, a visa is not a sufficient basis for entering the country. Consular fee - $28.
CUSTOMS RULES: The number of imported and exported means of payment is not limited. Cash and securities worth FRF50,000 or more must be declared. Foreign currency converted into francs can only be re-converted into foreign currency up to the equivalent of 5,000 francs.
INFORMATION TELEPHONE throughout France - 12. Firefighters - 18. Police - 17. Ambulance - 15.
French Republic- a state in Western Europe. The motto of the Republic is “Liberty, Equality, Fraternity”, its principle is government of the people, by the people and for the people. On October 4th, 1958, the Fifth Republic was established in France. Since 2012, the President of France is Francois Hollande. The capital is the city of Paris. France is a nuclear power and one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council. Since the 1950s, France has been one of the states participating in the creation of the European Union. The territory of the French Republic occupies 674,685 km².
The population of France numbered 63.8 million inhabitants in 2008, and in January 2010 - 65.4 million people. 62.8 million people live on the continental territory. In terms of population, the state ranks 20th among 193 UN member countries.
The population density in France is 116 people/km². According to this indicator, the country ranks 14th among EU countries. The total fertility rate in France is one of the highest in Europe - 2.01 children per woman of reproductive age. Believers are predominantly Catholics (over 76 percent). The legislative body is a bicameral parliament (Senate and National Assembly). Administrative division: 27 regions (22 metropolitan and 5 overseas regions), including 101 departments (96 metropolitan and 5 overseas departments).
Industry. Iron and uranium ores and bauxite are being mined. The leading branches of the manufacturing industry are mechanical engineering, including automotive, electrical and electronic (TVs, washing machines, etc.), aviation, shipbuilding (tankers, sea ferries) and machine tool building. France is one of the world's largest producers of chemical and petrochemical products (including caustic soda, synthetic rubber, plastics, mineral fertilizers, pharmaceutical products and others), ferrous and non-ferrous (aluminum, lead and zinc) metals. French clothing, shoes, jewelry, perfumes and cosmetics, cognacs, and cheeses (about 400 varieties are produced) are very famous on the world market.
France is a highly developed industrial-agrarian country and occupies one of the leading places in the world in terms of industrial production. The gross domestic product stands at 1.9 trillion euros in 2009. GDP per capita in the same year was 30,691 euros. France is the 6th economic power in the world after the USA, China, Japan, Germany and Great Britain.
Railway transport . Rail transport in France is very developed. Local and night trains, including TGV (Trains a Grande Vitesse - high-speed trains) connect the capital with all major cities of the country, as well as with neighboring countries Europe. The speed of these trains is 320 km/h. France's railway network is 29,370 kilometers long, making it the longest railway network in Western Europe. There are rail connections with all neighboring countries except Andorra.
Metro in France is available in Paris, Lyon, Marseille, Lille, Toulouse, Rennes. In Rouen there is a partially underground high-speed tram. In addition to the metro system, Paris has a network of RER (Reseau Express Regional), connected to both the metro system and the commuter train network.
The climate in France is predominantly temperate, providing mild temperatures throughout the year.
The territory of France, called "l"Hexagone", i.e. "hexagon", is divided into 4 climatic zones:
Mild and humid oceanic climate with cool summer in the west along the Bayonne - Lille line;
Mountain climate with harsh winters and hot summers in Alsace, Lorraine, along the Rhone Valley and in the mountain ranges (Alps, Pyrenees, Massif Central);
Temperate continental climate in the north, in Paris and central region where there are cool winters and warm summers;
The south of the country belongs to the Mediterranean climate zone with warm winters and hot summers.
The weather in France is also predictable - it rarely experiences sudden changes, and usually does not reach the extremes of too hot or too cold temperatures. In summer the weather in France is dry, but this effect is mitigated by the westerly wind, which brings freshness. In winter, the weather in France is relatively warm and it rarely snows. Walnut, birch, oak, spruce, and cork trees grow in the forests, which occupy about a quarter of the country's territory. On the Mediterranean coast there are palm trees and citrus fruits. Among the representatives of the fauna, deer and fox stand out. Roe deer live in alpine regions, and wild boar survive in remote forests. A large number of different species of birds, including migratory ones. Reptiles are rare, and among snakes only one is poisonous - the viper. Many types of fish live in coastal sea waters: herring, cod, tuna, sardine, mackerel, flounder, silver hake.
The relief of France is very diverse, contributing to the active development of ski tourism and mountaineering. The highest point in France is Mont Blanc - 4800 m (Alps), and accordingly it is also the highest point in Europe. Also on the territory of France, there is part of the Pyrenees mountain range. Thus, the Alps separate France from Italy and Switzerland, and the Pyrenees from Spain. The north of the country is presented in the form of plains and incredible beauty of river valleys.
National holidays in France. In France 10 holidays. Holidays in France are January 1, May 1 and 8, Easter Monday, Ascension, July 14, August 15, November 1 and 11 and December 25. These days, most institutions, banks, and shops are closed. Five times a year, French schoolchildren and students go on vacation: a week for All Saints' Day (at the end of October), two weeks for Christmas, another two in February and spring, and, of course, in the summer in July and August. During these periods, tourist spots and streets become more crowded.
Timezone. From the end of March to the end of October, clocks in France are switched from GMT+1 to GMT+2 (GMT= Greenwich Meridian Time - Greenwich time corresponding to the prime meridian of longitude).
In the departments of metropolitan France, from 2002 onwards, the period of summer time begins on the last Sunday in March at 02:00. At this point the clock moves forward one hour.
Daylight saving time ends on the last Sunday in October. At 03:00 the clock is set back an hour.
The area of France is 551.5 thousand square meters. km, population - 59.5 million people in 2001. In terms of area, France is the third country in Europe (after Russia and Ukraine) and the first in Western Europe (about a fifth of the territory of the European Union), more than twice the area of Great Britain.
In 2000, France ranked fifth in the world in terms of GDP production after the USA, Japan, Germany and Great Britain. Its GDP was $1,294.2 billion (per capita 24,223 per year in 2000 PPP dollars).
France occupies the extreme western part of the European continent and the configuration of the territory resembles a hexagon with maximum distances of no more than 1000 km, and there is not a single settlement more than 50 km away from the sea coast or river bed.
France owns the island of Corsica and a number of small coastal islands in the Mediterranean Sea, as well as overseas departments and territories - Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint-Pierre and Mequelon, Reunion, French Guiana, New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna - with total area 127 thousand sq km, with a population of 1.5 million people. For comparison: on the eve of the Second World War, France's possessions (including trust territories) amounted to 12 million square meters. km with a population of 70 million people.
France can be called an Atlantic and Mediterranean country, a Rhineland and Pyrenean country. Convenience of sea and land connections, hub geographical position among the largest Western European states, in the vicinity of the economic centers of the region (South-East England, Rhineland Germany, Western Switzerland, north-west Italy) contributed to the early development of its economy, the growth of trade and cultural relations. However, this geographical location was also one of the reasons for the repeated invasion of its territory by foreign conquerors.
Natural conditions and resources. Main Differences natural conditions France, like Germany, is caused by a gradual rise in surface from north to south. The entire northern and western part, that is, almost half of the country, is occupied by lowlands. These are areas of former subsidence of the earth's crust, filled with sedimentary deposits. The most extensive of them are the North French (Aquitaine) Lowland - the main living area of the country. Significant oil deposits are associated with sedimentary deposits of the Aquitaine Lowland. In the central, northeastern and northwestern regions there are ancient Hercynian massifs: the Central French Massif, the Vosges, the Ardennes, and the Armorican massif, formed more than 200 million years ago. Many minerals are associated with these geological structures.
In the south and southwest rise the young mountains of the Alpine folding - the Alps and the Pyrenees. These mountain systems have large reserves of water, their vast alpine and subalpine meadows are used for pastures, and forests provide raw materials for the wood processing industry. Basic mineral resources France - these are iron ores, bauxite, tungsten, lead, tin, silver. However, the country is not rich enough in energy resources: reserves of coal, oil and gas are insignificant. More important are the uranium reserves in the Massif Central and the energy of mountain rivers, in particular the Rhone and its Alpine tributaries. In perspective great opportunities in using the energy of sea tides, which reach 12–16 meters in height off the coast of France. The most important mineral resources are located on the outskirts of the country. Deposits of coal, potash and rock salts are located in the northeast of the country (Alsace). There is a lot of iron ore in Lorraine, but it is poor in iron content. In the south of the country - in Provence and Languedoc - there are bauxites, but their mining is currently suspended due to unprofitability. France is rich in natural building materials.
The climate of France is formed under the influence of Atlantic air masses and is characterized as maritime, moderately warm and humid. In most of the country (excluding the mountains), winter temperatures are positive, there is usually no snow cover, and the rivers do not freeze. Annual precipitation is 600–1000 mm. Only in the north-west of the country (Brittany) does agriculture suffer from excess moisture, and on the coast Mediterranean Sea(Mediterranean climate type) - from lack of moisture in the summer. The mildest winter is the extreme East End coast of France - Riviera (in Nice average temperature July +230, January +80). Climatic conditions allow you to grow crops from both the temperate zone and the subtropics (citrus fruits in Corsica).
France has many rivers, but few lakes. Rivers have large reserves of hydroelectric power, especially the Rhone and its tributaries, which account for half of the hydropower reserves, and the rivers of the Massif Central - 20%.
The soils are brown forest, humus-carbonate, quite fertile, especially the soils of the North French Lowland.
France is a country of international tourism and mountaineering. Favorable climate, historical and architectural monuments, huge opportunities for the development of mountaineering and winter sports in the mountains, dense network good roads, hotels and restaurants attract tens of millions of foreigners, and all this brings large revenues to the country.
The nature of France is highly cultivated by man: 33% of the area is arable land; 27% – forests (mostly planted); 21% – pastures and hayfields; 2.5% – vineyards, orchards and vegetable gardens; 17% – developed and unused land.
Population. Political system. France is a country of relatively homogeneous ethnic composition. About 97% of its population are French, one of the Romance peoples of Europe. In ancient times, the territory of France was inhabited by Gauls (Celts), hence its ancient name - Gaul. The Gauls later mixed with the Roman conquerors and Germanic tribes. The name "French", like "France", comes from the Germanic tribe of the Franks, who conquered in the 5th century. BC. northern part countries.
Other national minorities - Alsatians and Lorraineers, Basques, Corsicans live on the periphery of the country, as well as immigrants (Italians, Portuguese, Moroccans, Algerians, etc.). They make up more than 4 million people – 7–8% of the total population. France's population is growing faster than other large European countries as the government encourages higher birth rates and immigration. France has welcomed immigrants throughout its history. France's population is 1% of the population globe(17th place in the world). The average birth rate in 2000 was 12.3/1000, mortality rate – 9.1/1000, infant mortality rate – 4.5/1000. The average life expectancy in 2000 was 78.8 years, including: men – 74.8, women – 82.9 years. The working-age population makes up 42% of the total, in the USA this figure is 48%, in Japan - 49%. Women make up 51.3% of the country's population.
Social class structure of the population: 85% of the workforce are wage earners (workers and employees), 12% are small entrepreneurs in towns and villages and helping family members, and about 3% are large business employers who control the bulk of the national wealth and politics of France. The standard of living of the population is approximately the same as in Germany and Great Britain, but 2–2.5 times higher than in modern Russia.
Almost all religions are represented in France, however, among believers, Catholics make up 81.2% of the total population, Muslims - 6.9%, Protestants - 1.6%, Orthodox - 0.3%, other religions - 10%. The influence of the church is weaker than in Italy and Spain.
In France, compulsory free education is provided for children from 6 to 16 years of age, but secondary education is largely different from other European countries and consists of the following levels: mother's school (corresponding to our kindergartens), primary, college, lyceum and high school. The peculiarity of the education system is that the state is responsible for the content and organization of education, provides professional training, recruitment, management and remuneration of teachers. Along with state educational institutions, there are also private ones, especially those providing denominational (Catholic) education; they cover about 20% of students. The entire education system is characterized by a differentiated approach to students' abilities, an informal atmosphere in educational groups and a trusting relationship with teachers. Education is secular in nature and built on the principles of political, ideological and religious impartiality.
In 1998, the number of schoolchildren and students exceeded 15 million people, accounting for a quarter of the country's population. In addition, the education system is the largest employer, employing over 1.2 million people - just over half of the total number of government employees. Government spending on education amounts to 7.4% of GDP.
Three quarters of the population lives in cities, with half in individual residential buildings. The main form of urban settlement is agglomeration, and in rural areas small villages and hamlets are typical. There are 52 agglomerations (urban areas) in France, which account for about 60% of all city residents. Five of them are the largest. The Paris metropolitan area is home to 10.6 million people, or 17.5% of the country's population. In France, as in Great Britain, the importance of the capital is exceptionally great, which stands out sharply in terms of the number of inhabitants among other centers. The next largest agglomerations are Lyon (1.6 million people), Marseille (1.4 million people), Lille (1.1 million people), Toulouse (0.9 million people); they are 7–10 times inferior to Paris. Therefore, the government of the country is pursuing a policy of curbing the growth of Paris. The construction of new factories and other facilities is limited here, and the development of other economic regions and centers is stimulated.
France is a presidential republic. The constitution of 1958 with amendments is in force.
The head of state is the president, elected for a term of 7 years by direct universal suffrage, endowed with broad powers: he appoints members of the government, is the supreme commander in chief, and has the right to dissolve the National Assembly.
The highest legislative body is the parliament, consisting of two chambers - the National Assembly, elected for a period of 5 years, and the Senate; senators are elected for 9 years; Every three years the composition of the Senate is renewed by one third.
The government is responsible to parliament and may be subject to a vote of no confidence by the National Assembly. This requires an absolute majority of votes of all deputies.
France is divided into 96 departments and 36.6 thousand communes. In most cases, departments are named after the rivers and mountains located on their territory. National minorities, with the exception of Corsicans, do not have autonomy.
Largest political parties: French Socialist Party, Rally for the Republic, Union for French Democracy, Communist Party of France, National Front.
FRANCE, GENERAL INFORMATION.
Official name: France, French Republic (République française French),
French Republic
Based: 843 (Treaty of Verdun) from 1958 - Fifth Republic.
Capital: Paris.
Official language: French.
Currency unit: Euro.
Political system: presidential-parliamentary republic.
Head of State: The president.
Head of the government: Prime Minister
Parliament: bicameral (Senate and National Assembly).
Square: 674.8 thousand sq. km, ranks 48th in the world.
Population: 65.4 million people.
Population density: 115 people per 1 sq. km.
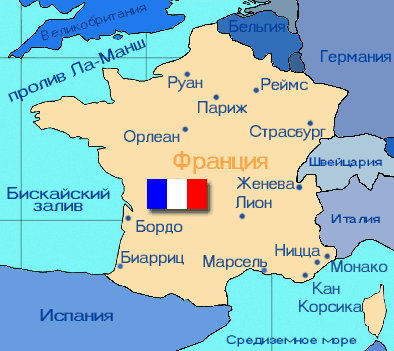
Information about France. Description of France.
France simply cannot help but attract people, because it is the center of fashion, culture, the birthplace of love. It is therefore not surprising that 60 million tourists come to France every year. In France you will not be bored at any time of the year and everyone will find something for themselves. They combine here beautiful beaches Cote d'Azur and ski resorts French Alps. Culture connoisseurs will be able to visit the unique collections of the museums of the Louvre, Montmartre, Picasso, Rodin and many others. Most cities in France are of great interest in themselves. The nature of the country is no less beautiful than the architecture of the cities, numerous vineyards, health resorts... here you will find everything you could want.
It might be useful to read:
- How to get on an excursion to Antarctica?;
- Czech Republic Troy Castle. Troja Castle in Prague. Ancient winery and museum;
- Böcklin and his “island of the dead” A cultural phenomenon of its time;
- Air tickets to Crimea Air tickets to Crimea will become cheaper;
- What you can and cannot take with you;
- Open left menu Heviz How to get from Budapest to Lake Heviz;
- Cable car in Nha Trang (Vinpearl) The longest cable car in the world Vietnam;
- Kamenets-Podolsk fortress - a historical monument of Ukraine Life outside the walls of the Kamenets-Podolsk fortress;